SonarQube Quality Metrics Review
Prefrace
Below you can find sample of how SonarQube service can be calibrated for a need of a specific project.
Introduction
SonarQube is using SQALE (Software Quality Assessment based on Lifecycle Expectations) model in order to determine quality of the source code.
Main characteristic of the SQALE model are:
-
The SQALE Quality Model is based on ISO 9126
-
The SQALE Method’s Quality Model takes the software’s lifecycle into account.
-
The SQALE method provides common language to all teams. Its metrics can be used for any technology. And analysis results are comparable.
According to the SQALE each organization has to define it’s own concrete definition of the right code. As well as calibrate the metrics to adjust project-specific parameters.
In this document next SQALE elements will be reviewed taking in account Vodoo project requirements:
-
SQALE Technical Debt Pyramid
-
Platform specific rules Severity
-
SQALE Rating definition
Reviewing procedure was done by Expert Team. Expert Team consisted from iOS, Android, Web domains experts and Vodoo management staff.
SQALE Technical Debt Pyramid
According to ISO 9126 SQALE defines next Quality Model’s Characteristics
| Name |
|---|
| Reusability |
| Portability |
| Maintainability |
| Security |
| Efficiency |
| Changeability |
| Reliability |
| Testability |
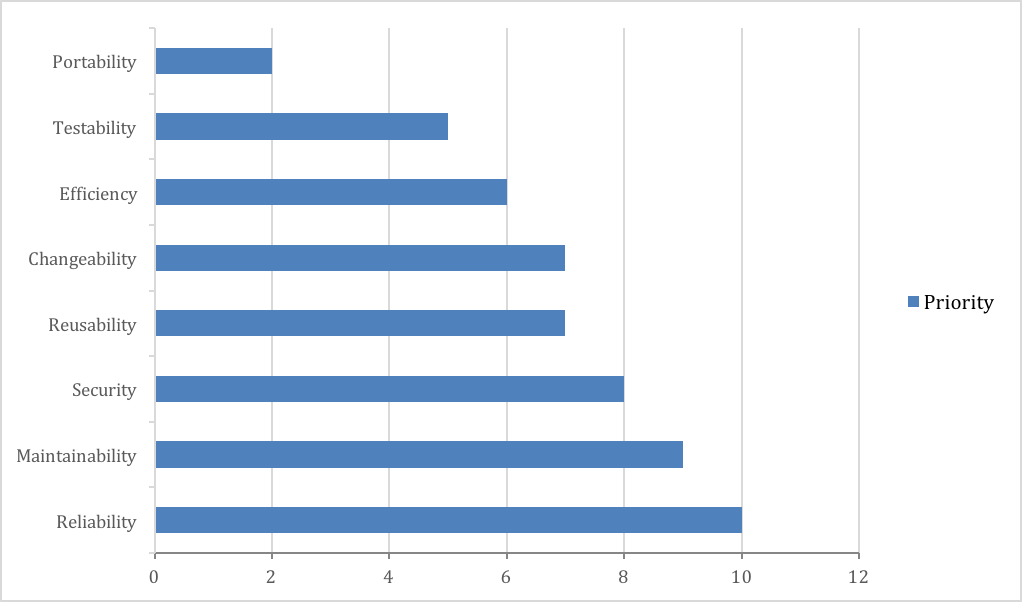
According to Vodoo project necessities Expert Team has defined next priorities for the Quality Characteristics
| Name | Priority (0-10) |
|---|---|
| Reusability | 10 |
| Portability | 9 |
| Maintainability | 8 |
| Security | 7 |
| Efficiency | 7 |
| Changeability | 6 |
| Reliability | 5 |
| Testability | 2 |
So Reliability characteristics are the most important one. And Portability is the least important one.
According the Prioritized Quality Characteristics next Technical Debt Pyramid was formed:
Technical Debt Pyramid
Quality Characteristics Priority can be changed according to the Business needs of the project.
Each Quality Characteristics has platform specific rules set associated with it. And they will be reviewed next.
Platform Specific Rules Set Severity Review
Each Quality Characteristics has platform specific rules set associated with it. And violations of these rules are used as an input to calculate Technical Debt of the project.
Also each rule has its severity. And the severity depends on Quality Characteristic type of the specific rule. In general higher Priority of the rule’s Quality Characteristic type - higher it’s severity should be.
According to the above-mentioned criteria the Expert Team has reviewed existing rule’s severity for iOS, Android, Web platforms.
Industrial standard rules set were taken as a baseline.
Reviewed Android Rules:
| No. | Name | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Classes should not be loaded dynamically | Blocker |
| 2 | Web applications should not have a “main” method | n/a |
| 3 | Exceptions should not be thrown from servlet methods | n/a |
| 4 | Untrusted data should not be stored in sessions | n/a |
| 5 | Return values should not be ignored when function calls don’t have any side effects | Major |
| 6 | Non-serializable classes should not be written | n/a |
| 7 | Fields in a “Serializable” class should either be transient or serializable | n/a |
| 8 | Servlets should not have mutable instance fields | n/a |
| 9 | HttpServletRequest.getRequestedSessionId() should not be used | n/a |
| 10 | Mutable members should not be stored or returned directly | Major |
| 11 | PreparedStatement and “ResultSet” methods should be called with valid indices | n/a |
| 12 | Instance methods should not write to “static” fields | Major |
| 13 | Calendars and “DateFormats” should not be static | Major |
| 14 | read and “readLine” return values should be used | Critical |
| 15 | Throwable.printStackTrace(…) should not be called | Minor |
| 16 | Dodgy - Immediate dereference of the result of readLine() | Major |
| 17 | Security - Servlet reflected cross site scripting vulnerability | n/a |
| 18 | Correctness - An apparent infinite recursive loop | Blocker |
| 19 | Dodgy - Unchecked/unconfirmed cast | n/a |
| 20 | Security - JSP reflected cross site scripting vulnerability | n/a |
| 21 | Security - Servlet reflected cross site scripting vulnerability | n/a |
Reviewed Web Rules:
| No. | Name | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | JSF expressions should be syntactically valid | n/a |
| 2 | “autocomplete” should be set to “off” on input elements of type “password” | Major |
| 3 | Javascript scriptlets should not have too many lines of code | Major |
| 4 | Web pages should not contain absolute URIs | Minor |
| 5 | Dynamic includes should not be used | n/a |
| 6 | Disallowed “taglibs” should not be used | n/a |
| 7 | Function calls should not pass extra arguments | Major |
| 8 | A “for” loop update clause should move the counter in the right direction | Major |
| 9 | Values should not be uselessly incremented | Major |
| 10 | “defaults” should be a function when objects or arrays are used | n/a |
| 11 | The “changed” property should not be manipulated directly | Major |
| 12 | “!important” annotation should be placed at the end of the declaration | Blocker |
Reviewed iOS Rules:
| No. | **Name ** | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Too many parameters | Major |
| 2 | Non case label in switch statement | Blocker |
| 3 | Empty else block | Critical |
| 4 | Goto statement | Blocker |
| 5 | Default label not last in switch statement | Blocker |
| 6 | Parameter reassignment | Critical |
| 7 | Replace with object subscripting | Major |
| 8 | Replace with boxed expression | Major |
| 9 | Unnecessary else statement | Blocker |
| 10 | High npath complexity | Critical |
| 11 | Must override hash with isEqual | Critical |
| 12 | Dead code | Critical |
| 13 | Collapsible if statements | Critical |
| 14 | Short variable name | Critical |
| 15 | Switch statements should have default | Critical |
| 16 | Replace with number literal | Major |
| 17 | Multiple unary operator | Critical |
| 18 | Redundant local variable | n/a |
| 19 | Replace with container literal | Major |
| 20 | Jumbled incrementer | Blocker |
| 21 | Redundant if statement | Major |
| 22 | For loop should be while loop | Critical |
| 23 | Unused method parameter | Minor |
| 24 | Missing break in switch statement | Blocker |
| 25 | Switch statements don’t need default when fully covered | n/a |
| 26 | Long variable name | Major |
| 27 | Empty try statement | Critical |
| 28 | Bitwise operator in conditional | n/a |
| 29 | Redundant nil check | Critical |
| 30 | Unused local variable | Minor |
| 31 | Feature envy | n/a |
| 32 | High cyclomatic complexity | Critical |
| 33 | Constant if expression | Critical |
The reviewed rule’s severity is going to determine the priority of the related Technical Debt “interest payment”.
Rule’s severity can be changed according to the Business needs.
SQALE Rating Definition
In order to relatively evaluate amount of Technical Debt in the project 2 metrics were taken into the consideration:
-
Technical Debt Ratio
-
SQALE Rating
Technical Debt Ratio - is the relationship between estimated technical debt amount and estimated project amount. For instance:
Technical Debt - 5 m/d
Project Duration - 100 m/d
Technical Debt Ratio = Technical Debt / Project Duration
Technical Debt Ratio = 5 / 100 = 5%
Technical Debt is calculated based on amount of violated Rules for a specific platform.
Next table determines relationship between SQALE Rating and Technical Debt Ratio:
| SQALE Rating | Technical Debt Ratio |
|---|---|
| A | 0 - 5% |
| B | 5% - 10% |
| C | 10% - 20% |
| D | 20% - 50% |
| E | 50% - 100% |
The relationship is the industrial standard set by SonarQube.
The relationship can be reviewed according to the Business needs of the specific project.
Conclusion
SonarQube is using SQALE model to measure quality of the software product. SQALE model is the projection of the ISO 9126. This quality model is provides common quality metrics for the different platforms used in the project. Quality metrics are defined by the set of Quality Characteristics and platform specific pules sets. Priority of these parameters is based on conclusions of the Expert Team. And can be adjusted according to the Business needs.
SQALE Rating and Technical Debt Ratio are cumulative metrics that can be used in order to evaluate project quality and compare one project to another.
This document can be used as a baseline for Vodoo project quality assessment.
Reference Documents
The SQALE Method Definition Document; Author: Jean-Louis Letouzey Version: 1.0 January 27, 2012 The SQALE method for evaluating Technical Debt; Letouzey, J.-L.